✍️ In This Issue ✍️
This Week in AI: NVIDIA, Microsoft, OpenAI Alphabet and more
Deep Dive: The Living Intelligence: How AI and Biotechnology Are Merging to Reshape the Future
AI Tools We Love: ChatGPT Tasks
Culture Corner: Gattaca
Quote for You: Martin Rees💡
This Week in AI
NVIDIA
🚧 Nvidia puts safety first with new tools for AI agents. These features help developers add guardrails against jailbreaks and other exploits, ensuring AI systems behave as intended. It’s a bid to boost trust as AI finds its way into more critical applications.
🏛️ iGenius and Nvidia team up for regulated industries. The Italian AI company collaborated with Nvidia on a 355B-parameter model designed for sectors like finance and healthcare, where compliance is king. By focusing on safety and reliability, they hope to expand AI’s reach into heavily regulated spaces.
Microsoft
🔬 Microsoft’s new MatterGen platform is turning sci-fi into tangible materials. It uses AI to create substances with mechanical, chemical, and magnetic properties that could transform everything from solar cells to carbon capture. Just like the discovery of lithium cobalt oxide fueled smartphone tech in the ’80s, MatterGen could define the next wave of material breakthroughs. This is another step for AI entering the real physical world.
Source: Microsoft
🏗️ Microsoft’s AutoGen v4 lets developers build custom AI agent teams. Asynchronous messaging keeps bots in sync, even if they’re coded in different languages. With improved decision tracking and broader workspace access, developers have more power to orchestrate multiple AI agents at once.
OpenAI
🗄️ OpenAI adds finance heavyweight Adebayo Ogunlesi to its board. The BlackRock executive will guide the company’s global expansion, including critical data center builds. It’s a strategic move as OpenAI positions itself for rapid international growth.
Adebayo Ogunlesi, Source: Wikipedia
🤖 OpenAI targets general-purpose robotics for real-world AGI. The company is hiring robotics talent to push ChatGPT-like intelligence into physical settings. Having already invested in humanoid-robot startup Figure AI, OpenAI’s move signals a deepening focus on embodied AI.
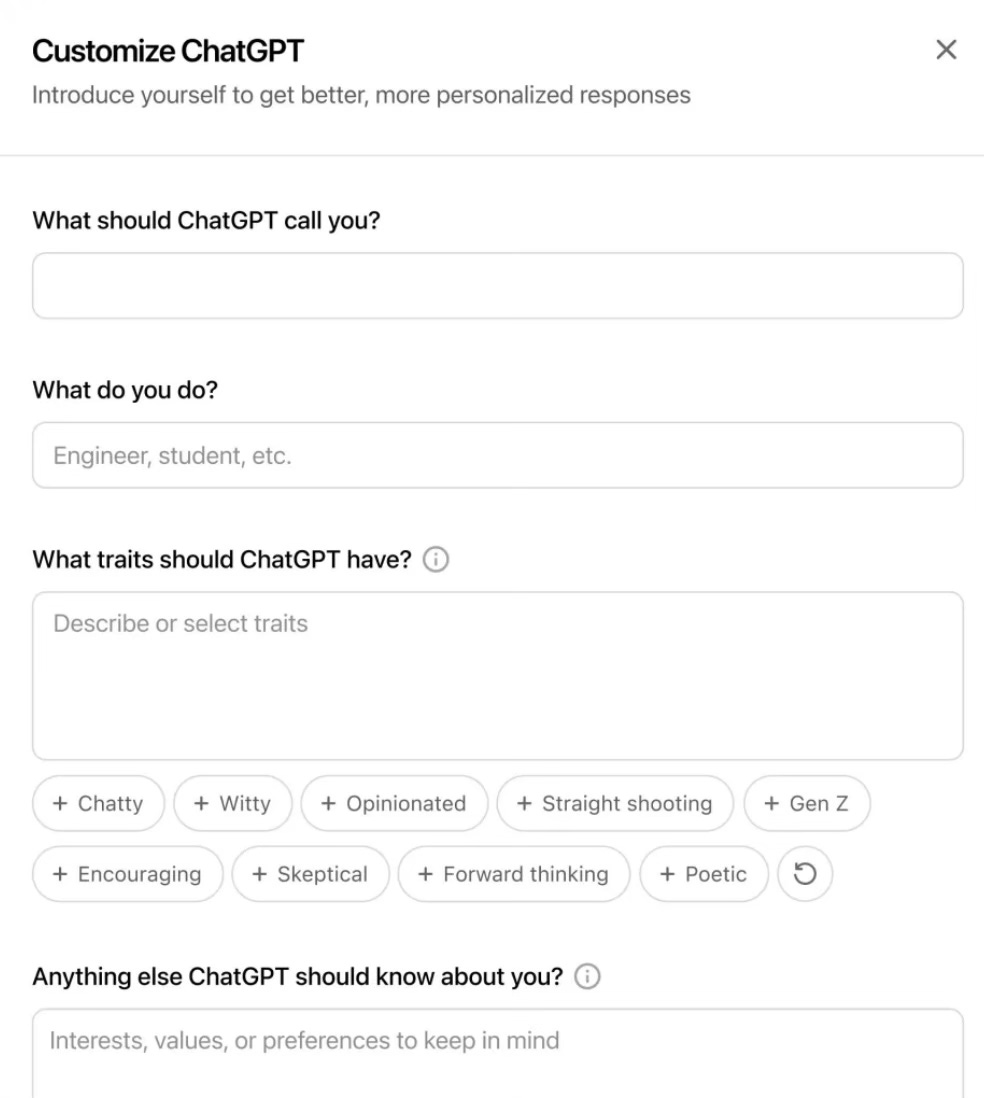
📝 ChatGPT could soon match your vibe — Gen Z, skeptic, or anything in between. A briefly spotted feature showed users can infuse ChatGPT with various traits, plus share personal details like profession and preferred name. OpenAI seems to be taking cues from competitors that already let users design custom chatbot personas.
🏆 UC Berkeley’s Sky-T1-32B-Preview model claims to rival OpenAI’s o1 reasoning. Trained in just 19 hours on 8 H100 GPUs for about $450, it’s a bold feat of optimization if true. You can find more details on the model, training methods, and data here.
Alphabet
🛑 Alphabet refuses to fact-check as EU disinformation laws loom. The tech giant is pushing back against upcoming regulations that would require stricter oversight of search results and YouTube videos. It’s a standoff that could redefine how big tech handles misinformation in Europe.
🤹 Alphabet’s Gemini proves it can juggle multiple media streams. In a world-first, an experimental version of the model analyzed multiple video feeds and static images simultaneously. This multitasking ability could pave the way for next-level content understanding and generation.
💼 Google Workspace promises free AI features but raises prices anyway. Alphabet announced it’s bringing its entire AI stack — including Gmail summaries, a NotebookLM research assistant, and the Gemini chatbot — to Workspace at no extra charge. Yet monthly plans will still jump by $2 per user, while Microsoft relaunches Copilot Chat with a free interface and pay-as-you-go AI agents.
Others
🔎 France’s Mistral partners with AFP for real-time content verification. Instead of simply ignoring regulations, Mistral will feed its Le Chat chatbot 2,000 articles per day from the AFP news agency. The goal: give AI a daily dose of credible journalism to flag misinformation faster.
🎏 Duolingo sees a Mandarin boom amid TikTok’s uncertain future. It reported a 216% spike in Chinese-language learners (See: sassy tweet) as users explore alternatives like RedNote following TikTok’s planned Sunday shutdown. The trend signals a new wave of interest in Mandarin, both for cultural and practical reasons.
Source: X
🍀 LinkedIn debuts AI-powered ‘Jobs Match’ and CV-scanning tools. The new job-finder feature pinpoints positions worth applying for, while an AI agent helps businesses sift through applicant mountains. It’s part of LinkedIn’s push to streamline recruiting with intelligent automation.
🏁 AI zooms down the runway at 177 mph in a convertible Maserati. Italian researchers tested their experimental driving model at top speed, proving it can handle high-velocity decisions. Next stop: Florida’s Cape Canaveral, where they hope to set a new speed record.
Source: Maserati
📱 Amazon grapples with AI-powered Alexa updates for older devices. The head of AGI revealed challenges in ensuring new features work on 100 million existing Alexa units. The delay underscores the complexity of retrofitting hardware for advanced AI capabilities.
🌏 Meta’s SeamlessM4T makes real-time voice translation more fluent than ever. Instead of converting speech into text first, this new AI model translates your voice directly across languages, boosting accuracy by about 23%. With support for up to 101 languages, it’s a big leap toward breaking language barriers worldwide.
⚡ MiniMax-01 is shaking up the open-source scene with long-context AI. The Singapore-based company’s new model processes nearly 4M tokens at once — think the length of a small library. Its “Lightning Attention” mechanism helps it process data at 20–32x the capacity of other models, all at a fraction of the cost.
🏅 AI luminary François Chollet enters the AGI race with startup Ndea. Best known for his work on the tough-as-nails ARC-AGI benchmark, Chollet is now building a model that can excel at his own test. By using program synthesis and learning from only a few examples, Ndea aims to push LLMs closer to human-level intelligence.
💡 YouTube is testing a Gemini Live chat feature for videos. Coders discovered hidden references to a tool that would let users ask real-time questions about video content. Rumor has it a similar feature could soon land for PDFs as well.
📊 AI stocks climb as inflation shows signs of cooling. The last trading day before the inauguration of President Trump closed with huge jump, riding optimism in the tech sector. Quantum-focused companies also skyrocketed after a Microsoft blog post hyped the emerging field, with Quantum Computing Inc. jumping 55.45% in one day.
The Living Intelligence: How AI and Biotechnology Are Merging to Reshape the Future
One day, a scientist arrives at a laboratory and, with a simple voice command, sets in motion a series of experiments on microscopic tissue samples. Robotic arms move gracefully beneath the glow of LED lights, shifting tiny vials of experimental compounds. An artificial intelligence (AI) platform monitors every step, analyzing results in real time and adjusting the next wave of tests on the fly. This may sound like science fiction, but such “living” labs are already here—or rapidly on the way.
In a 2025 Harvard Business Review article, “Why Living Intelligence Is the Next Big Thing,” the authors describe how the huge megatrend like AI, and the less evident biotechnology and sensors converge, enabling businesses employ ever-evolving systems that learn from each experiment, transaction, and market fluctuation. Data-driven algorithms and biological insight are creating a continuous feedback loop of discovery. This is what we mean by Living Intelligence—not just a buzzword, but a new paradigm for how we innovate and grow.
The Rise of the “Living” Lab
Historically, biotechnology has been slowed by lengthy, step-by-step processes. Research could take years to move from hypothesis to data collection, through countless experiments, then finally into clinical trials. By the time results were published, competitors or market forces might have shifted, leaving labs scrambling to catch up. Today, however, the synergy between AI and biotech offers a revolutionary overhaul of that timeline.
A case in point is Recursion Pharmaceuticals, a company that uses AI-driven platforms and robots to screen thousands of molecules across various disease models in parallel.
Source: Recursion Pharmaceuticals
Instead of waiting months for a single lab test to complete, Recursion can scan hundreds of cell types each day, with AI algorithms interpreting results almost instantly. If a compound shows promise for treating, say, a rare liver disorder, the system pivots to confirm those findings and refine the testing approach—much like how Netflix quickly revises its show recommendations based on a user’s viewing habits.
The same principle is evident at Ginkgo Bioworks, often dubbed the “organism company.” Ginkgo merges automated biological experimentation with cloud-based AI to design custom microbes that can produce pharmaceuticals, industrial enzymes, or even fragrances.
Reconfigurable, Automated, AI-driven Labs, Source: Ginkgo Bioworks
Adventures in Drug Discovery
One of the most tangible successes of Living Intelligence is the transformation of drug discovery. Take the work of Insilico Medicine, which blends AI with generative chemistry to identify molecules likely to be safe and effective.
Pharma.ai, Source: Insilico MEdicine
Their software, Pharma.ai can propose new compound structures, then instantly evaluate their pharmacological potential. The lab tests the winners, feeding the results back into the model, which “learns” from every success or failure.
We saw a dramatic illustration of AI’s power in 2020, when researchers at MIT used machine learning to identify a new antibiotic called halicin, shown to kill drug-resistant bacteria. Traditionally, scanning millions of molecules for possible antibiotic properties would have taken a dedicated team years, but the AI system cut that search to mere days. This lightning-fast feedback is emblematic of Living Intelligence at work: every experiment is analyzed and re-analyzed, with each finding improving the next generation of experiments.
OpenAI Enters the Longevity Arena
Another sign that Living Intelligence is going mainstream is OpenAI’s latest foray into longevity science.
Sam Altman, OpenAI's CEO is a huge fan of longevity. According to this article, he personally invested 180 mUSD into a company that aims to extend human lifespan by 10 years. (My concern, that super rich will evolve into a new, upgraded species is just getting closer...).
Now, OpenAI as a company takes the next step. According to a recent report in MIT Technology Review (2025), OpenAI has developed a model capable of sifting through vast genomic and proteomic datasets to uncover the complex biological signatures associated with aging. Much as you might ask ChatGPT a question and refine it further based on the answer, scientists can use OpenAI’s longevity model to pose research questions about aging pathways, review the model’s findings, and then feed in new experimental data for deeper insights.
This approach is particularly compelling in drug development for age-related diseases. Pharmaceutical researchers can upload large-scale data—ranging from clinical trials to population health studies—and let OpenAI’s model find connections that might otherwise remain hidden. The model “learns” from each new piece of data, adjusting its predictions and offering more targeted hypotheses for follow-up experiments. In essence, the tool acts like a virtual scientist that never tires, constantly refining its theories on how to extend healthy human lifespans.
Personalizing Medicine in Real Time
Imagine going to a clinic for a routine checkup. Instead of simply recording your vital signs, the doctor prescribes a medication that’s fine-tuned to your genetic makeup. Over the next week, a wearable sensor tracks how your body responds, sending data to an AI system that automatically adjusts dosages to optimize efficacy and minimize side effects. This is personalized medicine, and we’re already partway there.
Companies like Moderna and BioNTech leveraged AI not just to speed up research on mRNA vaccines but also to refine formulations based on real-world feedback. Data on how different populations responded to vaccine doses fed back into subsequent iterations. That’s living intelligence at a population scale: a feedback loop where everything—viral variants, vaccine tweaks, and patient outcomes—feeds into a collective learning process.
On an individual level, continuous glucose monitors (like those produced by Dexcom or the partnerships forged with smartwatch makers) highlight how real-time biological data can steer personalized care. If a patient’s blood sugar spikes during certain hours, the AI system adjusts medication or diet suggestions on the spot. Over time, these dynamic data streams build a holistic picture of a patient’s health, enabling far more proactive and precise interventions.
Unlocking CRISPR’s Full Potential
Genome editing via CRISPR has made headlines as a potential cure for everything from sickle cell disease to certain forms of cancer. Yet CRISPR isn’t foolproof, and “off-target” edits in the genome can have unintended consequences. Here, AI comes to the rescue again.
By comparing millions of genetic sequences, AI tools developed by companies like Beam Therapeutics and academic labs at MIT and the Broad Institute can predict where CRISPR might cut incorrectly. Each experiment—successful or otherwise—shows the AI which mutations are associated with which off-target effects, improving the predictive models. This iterative approach transforms a process once marked by guesswork into a near-real-time, data-driven refinement cycle—once again illustrating how biotech is adopting Living Intelligence at its core.
A Broader Vision of Living Intelligence
As more biotech labs adopt these AI-powered feedback loops, the lessons learned are influencing other sectors. Tech giants like Google DeepMind—famed for beating human champions in the game of Go—have applied their expertise to protein folding predictions, dramatically speeding up drug design. Meanwhile, Microsoft’s Healthcare NExT initiative is leveraging cloud computing and AI to help hospitals manage patient data in real time, improving everything from triage decisions to personalized care plans.
Why does all of this matter? Living Intelligence drives agility. It lets companies innovate faster and pivot more smoothly, whether they’re refining CRISPR therapies or launching a new e-commerce platform. And while biotech leads the way with its fascinating, high-stakes experiments, other industries—finance, supply chain management, manufacturing—can adopt similar continuous learning cycles. Every transaction, test, or product iteration is data that teaches the system how to improve.
Balancing Innovation with Ethics
However, this constant evolution also raises critical ethical and regulatory questions. The more data we collect—especially sensitive genetic or medical information—the more pressing it becomes to address privacy and consent. Biases in AI algorithms could worsen health disparities if they’re trained on incomplete datasets. And automated decision-making must still be paired with human oversight to ensure safety and moral accountability.
Regulators like the FDA and EMA walk a tightrope: they want to encourage innovation while protecting public welfare. In many ways, the regulatory environment is grappling with its own transformation—shifting from evaluating static data sets to monitoring continuous, living pipelines of evidence.
The Future Is Already Here
It’s tempting to think of Living Intelligence as a futuristic concept, but it’s already evident in everyday life. Netflix updates its user interface in real time based on viewer feedback; Tesla pushes over-the-air software updates that boost car performance overnight. In biotech, the stakes are higher—human health, after all, is on the line—but the core premise remains the same: continuous, data-driven adaptation.
With OpenAI now entering the race to crack human longevity, we may soon see “living” drug pipelines that connect digital health apps, research robots, hospital databases, and wearable sensors in one vast, coordinated ecosystem. Each day, the system improves, thanks to relentless machine learning guided by human expertise and ethical oversight. It’s no longer enough to respond to change; the key is to thrive in it—to evolve in real time as new data and discoveries emerge.
Imagine if all those developments will be combined with advanced robotics in the future. Mini robots, ot nano robots (nanobots) will be able to build or change everything around us - including our very own body and health.
Take a look at this amazing example, where micro robots change their environment.
Take it a step further: imagine even smaller robots, nanobots—tiny enough to travel through your veins—designed to remove plaque or identify and destroy cancer cells. Exciting, isn't it?
This is what awaits us: seamless, ongoing fusion of biological insight, computational power, sensors and robots enabling breakthroughs in weeks instead of years—and reshaping the notion of what’s possible in healthcare, life sciences, and beyond.
AI Tools We Love: ChatGPT Tasks
OpenAI debuts ‘Tasks,’ giving ChatGPT a taste of agentic powers. Subscribers can schedule reminders, news roundups, and even get prompts based on location or weather. It’s a new productivity twist for ChatGPT, available on the web for Plus, Team, and Pro users. See, how it works!
How to Access ChatGPT Tasks
Sign In to Your ChatGPT Account If you already have a ChatGPT account with Plus or Pro subscription, simply log in as usual. Look for the new “Tasks” tab or button on your main dashboard. If you don’t see it, ensure you’ve updated to the latest version or check your account settings for early-access or beta features.
Enable Tasks in Settings In the ChatGPT “Settings” menu, find the Tasks section. Toggle it on, review the privacy and permissions details, and confirm. If you’re part of a team or enterprise workspace, your administrator may need to enable the feature for your organization.
Integrate with Email & Calendar: Well, forget it for now. OpenAI does not offer integrations yet... So, for me it's not a real agent yet. It's a wannabe agent... If you want a real automation, you have to use external services like IFFT or Zapier, that can turn text prompt into actions, and place a Calendar entry for you, or write an email, and send it, too.
Once enabled, Tasks seamlessly becomes part of your regular ChatGPT interface. You can create new tasks, monitor progress, and collaborate without leaving ChatGPT.
How to Use ChatGPT Tasks
Create a Task To start, simply describe what you’d like to be reminded about or have done. For example, you can ask ChatGPT to remind you to follow up on a project next Tuesday. Tasks are not integrated into external calendars or email clients; rather, they operate within ChatGPT’s environment. Once you set a task, you can rely on ChatGPT to remind you about it at the appropriate time.
Track Progress As time goes on, you can check on your tasks by asking ChatGPT for a status update. This might involve reviewing your existing reminders, seeing what’s due soon, or adjusting the timing of tasks. The system remembers the tasks you’ve created and keeps them readily accessible when you need a quick overview.
Refine and Modify If you need to adjust a reminder, change the date, or add more details to a task, you can update it by simply telling ChatGPT. No need for complex menus or additional tools—everything is managed through a conversational interface.
Stay Notified and On Track When a task’s time comes due, ChatGPT will notify you within its own environment. It doesn’t send out external emails or update your online calendar, but it ensures you have a clear reminder at the right moment so you can take action promptly.
How It Helps You Stay Organized
ChatGPT Tasks works best when you’re looking for a simple, conversational way to manage your to-dos. While it’s not a direct substitute for an integrated calendar or project management tool, it provides a convenient and flexible method to stay on top of your responsibilities without having to switch between multiple platforms.
Integrations with typical office apps, email clients, calendars will be probably the next logical step in the evolution of Tasks. Let's see, how long does it take.
Culture Corner: Gattaca
In my deep dive article, I explored the growing intersection of biosciences and AI; now, in the Cultural Corner, I’ll introduce a favourite movie of mine that vividly imagines a bleak future shaped by these advancements.
Gattaca (1997), directed by Andrew Niccol, is a science fiction film set in a dystopian future where society is divided into genetically engineered “Valids” and naturally conceived “In-Valids.” The story follows Vincent Freeman (Ethan Hawke), an In-Valid born with a high likelihood of health problems and a limited life expectancy. Despite his genetic shortcomings, Vincent dreams of traveling to space. To achieve this, he assumes the identity of Jerome Morrow (Jude Law), a genetically perfect individual who has been paralyzed in an accident, using Jerome’s DNA samples to pass as a Valid. Vincent must navigate his double life while dealing with the scrutiny of his colleagues, including Irene Cassini (Uma Thurman), and the investigation of a murder that threatens to expose his secret.
The film delves deeply into the ethical implications of genetic engineering and the societal pressures that arise when life is preordained by DNA profiles. While Gattaca does not feature traditional AI, it incorporates the advanced computational technologies and bioinformatics that underlie this genetic stratification. These technologies perpetuate discrimination based on genetic "validity" and raise profound questions about human potential, free will, and the morality of engineering “perfect” individuals.
I really like Ethan Hawke, he's an excellent actor. For me, his performance in the "Before..." trilogy is absolutely unforgettable. Here he delivers a great performance in a completely different genre. What makes Gattaca so fascinating is its timeless exploration of identity and perseverance in the face of systemic oppression. It highlights how human spirit and determination can triumph over the deterministic view of genetics. By presenting a world where bioscience is both a tool of advancement and a source of division, Gattaca remains a compelling, thought-provoking piece that continues to resonate in today’s discussions about genetic technology and ethics.
Quote for You
“In this century, not only has science changed the world faster than ever, but in new and different ways. Targeted drugs, genetic modification, artificial intelligence, perhaps even implants into our brains—may change human beings themselves.” — Martin Rees
Martin Rees, Photograph by Roger Harris
Martin Rees, Baron Rees of Ludlow, born on June 23, 1942, in York, England, is a distinguished British cosmologist and astrophysicist. He has significantly contributed to our understanding of the universe, particularly in areas such as galaxy formation, black holes, and cosmic microwave background radiation. Rees has held several prestigious positions, including serving as the fifteenth Astronomer Royal since 1995, Master of Trinity College, Cambridge (2004–2012), and President of the Royal Society (2005–2010).
Throughout his career, he has authored over 500 research papers and numerous books aimed at both scientific and general audiences, reflecting his commitment to advancing and communicating scientific knowledge.
I hope, you liked this piece.
Thanks for reading!
✌️Until next time!
Zoltan
🚀 Join me on Substack for the full experience, including the archive, deep dives, resources and podcasts — for free! 🚀
👉 In case you missed something, check out my latest articles: